STL-GO: Spatio-Temporal Logic with Graph Operators for Distributed Systems with Multiple Network Topologies
Jul 20, 2025· ,,,,,·
1 min read
,,,,,·
1 min read
Yiqi Zhao
Xinyi Yu
Bardh Hoxha
Georgios Fainekos
Jyotirmoy v. Deshmukh
Lars Lindemann
Abstract
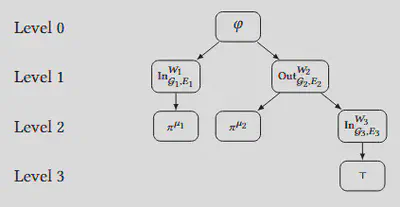
Multi-agent systems (MASs) consisting of a number of autonomous agents that communicate, coordinate, and jointly sense the environment to achieve complex missions can be found in a variety of applications such as robotics, smart cities, and internet-of-things applications. Modeling and monitoring MAS requirements to guarantee overall mission objectives, safety, and reliability is an important problem. Such requirements implicitly require reasoning about diverse sensing and communication modalities between agents, analysis of the dependencies between agent tasks, and the spatial or virtual distance between agents. To capture such rich MAS requirements, we model agent interactions via multiple directed graphs, and introduce a new logic – Spatio-Temporal Logic with Graph Operators (STL-GO). The key innovation in STL-GO are graph operators that enable us to reason about the number of agents along either the incoming or outgoing edges of the underlying interaction graph that satisfy a given property of interest; for example, the requirement that an agent should sense at least two neighboring agents whose task graphs indicate the ability to collaborate. We then propose novel distributed monitoring conditions for individual agents that use only local information to determine whether or not an STL-GO specification is satisfied. We compare the expressivity of STL-GO against existing spatio-temporal logic formalisms, and demonstrate the utility of STL-GO and our distributed monitors in a bike-sharing and a multi-drone case study.
Type
Publication
the ACM SIGBED International Conference on Embeddeed Software, 2025