Fairguard: Harness Logic-based Fairness Rules in Smart Cities
Abstract
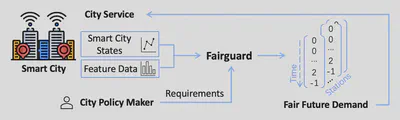
Smart cities operate on computational predictive frameworks that collect, aggregate, and utilize data from large-scale sensor networks. However, these frameworks are prone to multiple sources of data and algorithmic bias, which often lead to unfair prediction results. In this work, we first demonstrate that bias persists at a micro-level both temporally and spatially by studying real city data from Chattanooga, TN. To alleviate the issue of such bias, we introduce Fairguard, a micro-level temporal logic-based approach for fair smart city policy adjustment and generation in complex temporal-spatial domains. The Fairguard framework consists of two phases. First, we develop a static generator that is able to reduce data bias based on temporal logic conditions by minimizing correlations between selected attributes. Then, to ensure fairness in predictive algorithms, we design a dynamic component to regulate prediction results and generate future fair predictions by harnessing logic rules. Evaluations show that logic-enabled static Fairguard can effectively reduce the biased correlations while dynamic Fairguard can guarantee fairness on protected groups at run-time with minimal impact on overall performance.
Type
Publication
8th ACM/IEEE Conference on Internet of Things Design and Implementation